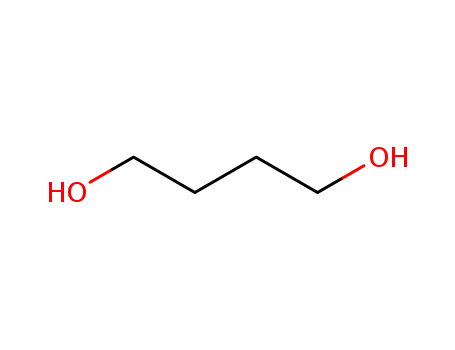
Product Details
110-63-4 Properties
- Molecular Formula:C4H10O2
- Molecular Weight:90.1222
- Appearance/Colour:viscous colourless liquid
- Vapor Pressure:0.015mmHg at 25°C
- Melting Point:20 °C
- Refractive Index:n20/D 1.445(lit.)
- Boiling Point:227.999 °C at 760 mmHg
- PKA:14.73±0.10(Predicted)
- Flash Point:105.909 °C
- PSA:40.46000
- Density:1.006 g/cm3
- LogP:-0.24880
110-63-4 Usage
InChI:InChI=1/C4H10O2/c5-3-1-2-4-6/h5-6H,1-4H2
110-63-4 Relevant articles
Effect of boron content on 1,4-butanediol production by hydrogenation of succinic acid over Re-Ru/BMC (boron-modified mesoporous carbon) catalysts
Kang, Ki Hyuk,Han, Seung Ju,Lee, Jong Won,Kim, Tae Hyeop,Song, In Kyu
, p. 206 - 213 (2016)
A series of Re-Ru bimetallic catalysts supported on mesoporous boron-modified carbon (denoted as Re-Ru/xBMC, x?=?B/C molar ratio) were prepared by a single-step surfactant-templating method and a subsequent incipient wetness impregnation method, and they were used for liquid-phase hydrogenation of succinic acid to 1,4-butandiol (BDO). The effect of boron addition on the catalytic activities and physicochemical properties of Re-Ru/xBMC catalysts was investigated. It was found that the addition of boron into carbon support affected surface area, metal dispersion, and reducibility of rhenium and ruthenium species in the Re-Ru/xBMC catalysts. It was also observed that boron species in carbon framework existed in several different phases such as substituted boron, partial oxidized boron, and boron oxide. In particular, the amount of substituted boron species was closely related to the hydrogen adsorption behavior of Re-Ru/xBMC catalysts. The amount of weak hydrogen-binding sites increased with increasing the amount of substituted boron species of the catalysts. Yield for BDO in the hydrogenation of succinic acid showed a volcano-shaped trend with respect to B/C molar ratio. This result was in good agreement with the amount of weak hydrogen-binding sites of the catalysts. It was revealed that TOFBDO increased with increasing the amount of weak hydrogen-binding sites of Re-Ru/xBMC catalysts. Among the catalysts, Re-Ru/0.04BMC with the largest amount of weak hydrogen-binding sites served as an efficient catalyst in the selective formation of BDO by hydrogenation of succinic acid.
Hydrogenation of γ-Butyrolactone to 1,4-Butanediol over CuCo/TiO2 Bimetallic Catalysts
Huang, Zhiwei,Barnett, Kevin J.,Chada, Joseph P.,Brentzel, Zachary J.,Xu, Zhuoran,Dumesic, James A.,Huber, George W.
, p. 8429 - 8440 (2017)
Titania-supported monometallic and bimetallic Cu-Co catalysts were prepared using (co)impregnation and studied for the hydrogenation of γ-butyrolactone (GBL) to 1,4-butanediol (BDO) at temperatures from 100 to 180 °C and a hydrogen pressure of 3.4 MPa. The highest catalytic activity occurred at a Cu:Co atomic ratio of 1:9 (Cu0.1Co0.9/TiO2), and a 95% yield of BDO was obtained. Characterization results showed mainly small nanoparticles (average size 2.6 nm) for pure Cu/TiO2, large particles (~19.8 nm) for pure Co/TiO2, and a bimodal particle size distribution of both small (~2.3 nm) and large (~16.5 nm) particles for the bimetallic catalyst with a Cu:Co ratio of 1:1. The addition of ~10 mol % Cu to Co/TiO2 increased the reducibility of the Co and resulted in the formation of core-shell CuCo bimetallic nanoparticles with a Co-rich core and Cu-rich shell. GBL hydrogenation in liquid ethanol and water produced an ester (ethyl 4-hydroxybutanoate) and a carboxylic acid (4-hydroxybutanoic acid) as the major products, respectively. GBL hydrogenation in 1,4-dioxane likely went through a 2-hydroxytetrahydrofuran (2-HTHF) intermediate. The 2-HTHF underwent facile ring-opening tautomerization to 4-hydroxybutanal (4-HB), followed by rapid hydrogenation to BDO at a reaction rate up to 700 times faster than GBL hydrogenation. The Cu0.1Co0.9/TiO2 catalyst maintained the BDO selectivity and about 80% of initial activity for GBL hydrogenation after 150 h time on stream in a continuous flow reactor.
Extremely facile and selective nickel-catalyzed allyl ether cleavage
Taniguchi, Takahiko,Ogasawara, Kunio
, p. 1136 - 1137 (1998)
Child's play! Allyl ethers as protecting groups for hydroxyl functions can be removed readily with a combination of DIBAL and catalytic amounts of [NiCl2(dppp)]. Propene is expelled in this remarkably selective reaction, and a nickel-catalyzed hydroalumination-elimination pathway is proposed. dppp = propane-1,3-diylbis(diphenylphosphane).
Thermodynamic equilibria between polyalcohols and cyclic ethers in high-temperature liquid water
Yamaguchi, Aritomo,Hiyoshi, Norihito,Sato, Osamu,Bando, Kyoko K.,Masuda, Yoshio,Shirai, Masayuki
, p. 2666 - 2668 (2009)
Thermodynamic equilibrium constants between polyalcohols and cyclic ethers in water at 573 K were determined by measuring their concentrations after the long-term reaction in a batch reactor. Intramolecular dehydration reactions of polyalcohols were important for conversion of biomass-derived carbohydrates; however, the yields of products were limited by thermodynamic equilibria between polyalcohols and products. All the thermodynamic equilibrium constants were estimated by the long-term dehydration reaction of 1 mol ·dm-3 polyalcohol aqueous solutions at 573 K. The thermodynamic equilibrium constants between butanepolyols or pentanepolyols and five-membered or six-membered cyclic ethers were within a range from (39 to 337) mol ·dm-3.
-
Enz,W.
, p. 206 - 212 (1961)
-
A temperature-controlled reversible ionic liquid - Water two phase - Single phase protocol for hydrogenation catalysis
Dyson,Ellis,Welton
, p. 705 - 708 (2001)
An ionic liquid - water system that undergoes a reversible two phase - single phase transformation dependent upon temperature has been used as a novel medium for the transition-metal-catalyzed hydrogenation of a water soluble substrate. At room temperature, the ionic liquid 1-octyl-3-methylimidizolium tetrafluoroborate, containing [Rh(η4-C7H8)(PPh3) 2][BF4] catalyst, forms a separate layer to water containing 2-butyne-1,4-diol. In a stirred autoclave the mixture was pressurized with hydrogen to 60 atm (1 atm = 101.325 kPa) and heated to 80°C giving a homogeneous single phase solution. On cooling to room temperature, two phases reform, with the ionic liquid phase containing the catalyst and the aqueous phase containing a mixture of 2-butene-1,4-diol and butane-1,4-diol products that can be simply removed without catalyst contamination.
Comparison of Carbon-13 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Methods for the Analysis of Multiple Partially Deuteriated Products from Catalytic Reactions: Heptan-1-ol and 2-Methylpropanol
MacDougall, Joanna K.,Simpson, Michael C.,Cole-Hamilton, David J.
, p. 3061 - 3066 (1994)
Products from the hydrocarbonylation of hex-1-ene or prop-2-en-1-ol using H2-CO or D2-CO in EtOH or EtOD have been analysed using 13C NMR techniques.Where there are up to four isotopomers in the products, analysis of β-shifted resonances in the 13C- NMR spectrum can give enough information for quantification of all isotopomers.Using prop-2-en-1-ol, D2-CO and EtOH, the 2-methylpropanol produced is a mixture of 16 different isotopomers.These can be individually quantified by analysis of the 13C- NMR spectrum.In particular, the resonance from the methyl C atom shows β and γ shifts, the latter being different for different types of γ-D atom.These analytical methods are shown to be superior to other possibilities including 1H NMR and mass spectrometry.
A Study of the Catalytic Deuteration of 1,4-Butynediol
Chickos, James S.,Uang, Jack Y.-J.,Keiderling, Tim A.
, p. 2594 - 2596 (1991)
-
High chemo and regioselective formation of alcohols from the hydrocarbonylation of alkenes using cooperative ligand effects
Boogaerts, Ine T.I. F.,White, Daniel F. S.,Cole-Hamilton, David J.
, p. 2194 - 2196 (2010)
The hydrocarbonylation of alkenes, including allyl alcohol, catalysed by rhodium complexes and wide angle bidentate ligands together with PEt 3, gives alcohols as the primary products with high chemo and regio-selectivity.
Continuous hydrogenation of 2-butyne-1,4-diol to 2-butene- and butane-1,4-diols
Rode,Tayade,Nadgeri,Jaganathan,Chaudhari
, p. 278 - 284 (2006)
Continuous catalytic hydrogenation of 2-butyne-1,4-diol (B3D) was carried out in a fixed-bed reactor over 1% Pt/CaCO3 catalyst to give 2-butene-1,4-diol (B2D) and butane-1,4-diol (B1D) without formation of any other side products. In case of continuous hydrogenation, higher selectivity (66%) to B2D could be obtained and the selectivity pattern was completely different from that found in case of batch slurry operation in which B1D selectivity was very much higher (83%) than the B2D selectivity (17%). Another interesting feature was that by varying the contact time, the selectivity to both B2D as well as B1D could be varied over a wide range which is an attractive option to obtain the desired products mix of B1D and B2D, depending on the fluctuation in the market demand. Further, a mathematical model for reactor performance was also developed on the basis of the kinetic data obtained previously in a batch slurry reactor. The predicted values of conversion, selectivity, and rate of hydrogenation were found to agree with the experimental data over a wide range of conditions.
A new carboxylesterase from Brevibacterium linens IFO 12171 responsible for the conversion of 1,4-butanediol diacrylate to 4-hydroxybutyl acrylate: Purification, characterization, gene cloning, and gene expression in Escherichia coli
Sakai, Yasuyoshi,Ishikawa, Junko,Fukasaka, Shunji,Yurimoto, Hiroya,Mitsui, Ryoji,Yanase, Hideshi,Kato, Nobuo
, p. 688 - 697 (1999)
A carboxylesterase that is responsible for conversion of 1,4-butanediol diacrylate (BDA) to 4-hydroxybutyl acrylate (4HBA) was found in Brevibacterium lines IFO 12171, and purified to homogeneity. The purified enzyme was active toward a variety of diesters of ethylene glycol, 1,4-butanediol, and 1,6-hexanediol. The Km and kcat of the enzyme for BDA were 3.04 mM and 203,000 s-1, respectively. The reaction with the purified enzyme gave 98 mM 4HBA from 100 mM BDA for 60 min. The enzyme gene was cloned from the chromosomal DNA of the bacterium. The open reading frame encoding the enzyme was 1176 bp long, corresponding to a protein of 393 amino acid residues (molecular mass=42,569Da). The deduced amino acid sequence contained the tetra peptide motif sequence, STTK, and the serine residue was confirmed to be the catalytic center of BDA esterase by site-directed mutagenesis for several amino acid residues. The gene was expressed in Escherichia coli under the control of the lac promoter, and the gene product (a fusion protein with 6 amino acid residues from β-galactosidase) showed the same catalytic properties as the enzyme from the parent strain.
Effect of Ethers on Reactions of Butylcoppers with α,β-Unsaturated Ketones in Toluene
Kingsbury, Celia L.,Smith, Robin A. J.
, p. 7637 - 7643 (1997)
Mixtures of butyllithium and copper iodide prepared in toluene react with α,β-unsaturated ketones predominantly in a 1,2-fashion. Addition of various ethers to the system results in some preference for the 1,4-product. The structural characteristics of ethers which influence 1,4-addition have been revealed. Reactions with chiral ethers did not alter the stereochemistry of the product. The results are correlated with the current views on the mechanism of organocuprate reactions.
A Novel and Unusual Reaction of Enol Ethers with Benzyltriethylammonium Borohydride and Chlorotrimethylsilane
Baskaran, S.,Chidambaram, N.,Narasimhan, N.,Chandrasekaran, S.
, p. 6371 - 6374 (1992)
Benzyltriethylammonium borohydride-chlorotrimethylsilane reagent system has been found to effect a novel and unusual reaction with cyclic and acyclic enol ethers 1 to give exclusively diols and alcohols 2 respectively in high yields, under very mild reaction conditions.
A Schiff Base Modified Pd Catalyst for Selective Hydrogenation of 2-Butyne-1,4-diol to 2-Butene-1,4-diol
Li, Haomeng,Wang, Xinkui,Chen, Xiao,Li, Chuang,Wang, Min,Yi, Yanhui,Ji, Min,Wang, Huilong,Shao, Zhengfeng,Liang, Changhai
, p. 2150 - 2157 (2020)
Abstract: Schiff-base modified Pd nanoparticles (NPs) supported on silica with an average size of ca. 2?nm have been synthesized via a one-pot aldimine condensation followed by impregnation-reduction of a palladium precursor, and the sample exhibits an excellent catalytic activity and selectivity in hydrogenation of 2-butyne-1,4-diol (BYD) to 2-butene-1,4-diol (BED). Under the mild reaction conditions (50?°C, 2?MPa H2, and 4?h) and additive-free, 95.2% BYD conversion has been achieved with ca. 100% BED selectivity over the Pd/SiO2–Schiff catalyst, and the Pd/SiO2–Schiff catalyst presents an excellent catalytic stability. The above results are much better than that of commercial Lindlar catalyst, and the improved catalytic performance is attributed to the strong metal–support interaction derived from the coordination of nitrogen sites (Schiff-base) to Pd NPs, based on catalyst characterization results. Graphic Abstract: Featured by additive-free and high selectivity, hydrogenation of 2-butyne-1,4-diol to 2-butene-1,4-diol over the Pd/SiO2–Schiff catalyst has been developed, aiming for green production of fine chemicals.[Figure not available: see fulltext.]
Bimetallic Synergy Effects of Phyllosilicate-Derived NiCu@SiO2 Catalysts for 1,4-Butynediol Direct Hydrogenation to 1,4-Butanediol
Wang, Changzhen,Tian, Yani,Wu, Ruifang,Li, Haitao,Yao, Benzhen,Zhao, Yongxiang,Xiao, Tiancun
, p. 4777 - 4787 (2019)
Hydrogenation of 1,4-butynediol (BYD) to 1,4-butanediol (BDO) is a two-step process, with an initial hydrogenation of BYD to 1,4-butenediol (BED) and the subsequent hydrogenation of BED to BDO. However, the BYD hydrogenation also involves many side reactions originated from the isomerization of BED. In order to inhibit the isomerization pathways, phyllosilicate-derived bimetallic NiCu@SiO2 catalysts have been developed for efficient C≡C/C=C hydrogenation in this work. Due to the formation of phyllosilicate matrix and highly dispersed metal nanoparticles, NiCu@SiO2 showed total BYD conversion with extremely high BDO selectivity compared to a conventional impregnated Ni/SiO2 catalyst. A remarkable result of NiCu@SiO2 catalysts is that a new type of bimetallic catalytic sites responsible for the high hydrogenation activity can be differentiated from the Ni phyllosilicate matrix by the induction of Cu species, and these neighboring bimetallic sites with the help of weak acid phyllosilicate interface, can realize to stabilize the activated BED species (allyl alcohol form) adsorbed on the cooperative active sites, thus to avoid its isomerization to aldehyde form and unexpected C=O hydrogenolysis. Consequently, it enhanced the selectivity to the diol products BDO significantly. Owing to the benign improvement of three center synergy effect, 9Ni1Cu@SiO2 possesses the optimum BYD direct hydrogenation ability with a rarely reported high selectivity of 90.5–94.5 % at 50 °C and 1 MPa.
Quantification of Interfacial pH Variation at Molecular Length Scales Using a Concurrent Non-Faradaic Reaction
Ryu, Jaeyune,Wuttig, Anna,Surendranath, Yogesh
, p. 9300 - 9304 (2018)
We quantified changes in interfacial pH local to the electrochemical double layer during electrocatalysis by using a concurrent non-faradaic probe reaction. In the absence of electrocatalysis, nanostructured Pt/C surfaces mediate the reaction of H2 with cis-2-butene-1,4-diol to form a mixture of 1,4-butanediol and n-butanol with selectivity that is linearly dependent on the bulk solution pH value. We show that kinetic branching occurs from a common surface-bound intermediate, ensuring that this probe reaction is uniquely sensitive to the interfacial pH value within molecular length scales of the surface. We used the pH-dependent selectivity of this reaction to track changes in interfacial pH during concurrent hydrogen oxidation electrocatalysis and found that the local pH value can vary dramatically (>3 units) relative to the bulk value even at modest current densities in well-buffered electrolytes. This study highlights the key role of interfacial pH variation in modulating inner-sphere electrocatalysis.
Modelling proposed intermediates in the hydrocarbonylation of alkenes catalysed by rhodium complexes of PBui3 and PPr i3
Cheliatsidou, Paraskevi,White, Daniel F. S.,Slawin, Alexandra M. Z.,Cole-Hamilton, David J.
, p. 2389 - 2394 (2008)
In ethanol, hydrocarbonylation reactions of alkenes catalysed by triethylphosphine complexes of rhodium give alcohols as the products with low linear selectivity, whilst rhodium complexes of PPri3 or PBui3 give mainly aldehydes, again with low linear selectivity. Modelling the proposed acyl intermediates by studying [Rh(C(O)Me)(CO)m(L)4-m] (L = PPri3 or PBui3) shows that they exist as monophosphine species under the normal reaction conditions. In the absence of CO, [Rh(=C(OH)Me)(CO) L2]+ can also be formed. The implications of these NMR studies for the chemo- and regio-selectivity of the hydrocarbonylation reactions are discussed. The Royal Society of Chemistry.
DIRECT SYNTHESIS OF 1,4-BUTANEDIOL FROM ALLYL ALCOHOL USING CARBON MONOXIDE AND WATER IN THE PRESENCE OF Rh6(CO)16-PROPANEDIAMINE SYSTEM
Kaneda, Kiyotomi,Imanaka, Toshinobu,Teranishi, Shiichiro
, p. 1465 - 1466 (1983)
Rh6(CO)16-propanediamine system catalyzes a direct route to 1,4-butanediol from allyl alcohol under the water gas shift reaction condition.Using an aminopyridine in place of the diamine gives γ-butyrolactone in a good yield.
An unusual reaction of cyclic enol ethers with titanium(III) tetrahydroborate
Ravikumar,Chandrasekaran, Srinivasan
, p. 2973 - 2978 (1997)
Titanium(III) Tetrahydroborate formed in situ from titanium tetrachloride and benzyltriethylammonium tetrahydroborate (1:4) readily reacts with cyclic enol ethers in dichloromethane at -20°C to give the corresponding acyclic diols in high yields after simple aqueous work-up.
Alkaline hydrolysis of oligomers of tartrate esters: Effect of a neighboring carboxyl on the reactivity of ester groups
Maniar,Kalonia,Simonelli
, p. 705 - 709 (1992)
The importance and the effect of neighboring groups on the hydrolysis of polymeric esters were demonstrated. Several oligomers of poly(butylene tartrate) were synthesized, and their kinetic behavior was studied under alkaline conditions. The oligomers and their degradation products were monitored by HPLC and identified by fast atom bombardment mass spectrometry. The rates of hydrolysis measured at pH 5-8 and at 75 °C indicate that the degradation of the oligomers obeyed pseudo-first-order kinetics. The rate of hydrolysis among the homologous series of oligomers increased as the molecular weight increased. However, the increase in hydrolysis rate was not proportional to the number of ester linkages in the oligomers. This deviation was explained on the basis of electrostatic repulsion of the neighboring carboxylate group toward the hydroxide ion. The calculations revealed that the electrostatic effect was so great that the ester linkage adjacent to the carboxylate anion did not contribute to the overall rate of hydrolysis. The technique presented here can be extended to any multifunctional-group compound that has repeat units and can undergo a specific reaction that can be accurately measured.
New environmentally friendly catalysts containing Pd-interstitial carbon made from Pd-glucose precursors for ultraselective hydrogenations in the liquid phase
Chan, Chun Wong Aaron,Xie, Yaling,Cailuo, Nick,Yu, Kai Man Kerry,Cookson, James,Bishop, Peter,Tsang, Shik Chi
, p. 7971 - 7973 (2011)
We report a novel preparation of a Pd nanocatalyst modified with subsurface C via blending a glucose precursor at the molecular level: the catalyst is demonstrated for the first time to be stereoselective in the hydrogenation of alkynes to cis-alkenes in the liquid phase.
Zirconium(IV) chloride catalyzed new and efficient protocol for the selective cleavage of p-methoxybenzyl ethers
Madhava Sharma, Gangavaram V.,Reddy, Ch. Govardhan,Krishna, Palakodety Radha
, p. 4574 - 4575 (2003)
A highly selective and efficient method for the unmasking of p-methoxybenzyl (PMB) ethers and esters has been developed by use of 20 mol % of zirconium(IV) chloride as Lewis acid in acetonitrile. The present method is very fast, and the conditions are tolerable to a variety of acid/ base-sensitive protecting groups and substrates such as carbohydrates, terpenes, and amino acids. The products are obtained in good to high yields.
Efficient Pd@MIL-101(Cr) hetero-catalysts for 2-butyne-1,4-diol hydrogenation exhibiting high selectivity
Yin, Dongdong,Li, Chuang,Ren, Hangxing,Shekhah, Osama,Liu, Jinxuan,Liang, Changhai
, p. 1626 - 1633 (2017)
Pd@MIL-101(Cr) hetero-catalysts have been successfully prepared using the metal-organic chemical vapour deposition (MOCVD) approach, by choosing [Pd(η3-C3H5)(η5-C5H5)] as a volatile precursor, and the hydrothermally stable metal-organic framework, MIL-101(Cr) as a support. The prepared Pd@MIL-101(Cr) hetero-catalysts characterized with various analytical techniques, exhibited highly monodispersed immobilized Pd nanoparticles in the MIL-101(Cr) cavities, while retaining the pristine crystallinity and porosity. The intact hybrid Pd@MIL-101(Cr) has been demonstrated to be an efficient catalyst for 2-butyne-1,4-diol hydrogenation with excellent activity, stability and selectivity (2-butene-1,4-diol (>94%)).
Aqueous phase hydrogenation of acetic acid to ethanol over Ir-MoO x/SiO2 catalyst
Wang, Zhiqiang,Li, Guangyi,Liu, Xiaoyan,Huang, Yanqiang,Wang, Aiqin,Chu, Wei,Wang, Xiaodong,Li, Ning
, p. 38 - 41 (2014)
Mo modified Ir/SiO2 (Ir-MoOx/SiO2) was firstly used for the aqueous-phase hydrogenation of acetic acid to ethanol and exhibited the best performance among the investigated catalysts. The synergy effect between the closely contacted Ir and Mo species is responsible for the excellent performance of Ir-MoOx/SiO2. Ir-MoO x/SiO2 is also effective for the hydrogenation of other biomass derived carboxylic acids. Especially when levulinic acid was used as the feedstock, high yields of 2-pentanol (39.0%) and 1,4-pentanediol (42.3%) were obtained simultaneously. To our knowledge, this is the first report about the direct hydrogenation of levulinic acid to 2-pentanol and 1,4-pentanediol over heterogeneous catalyst.
Biosynthesis of 1,4-butanediol from erythritol using whole-cell catalysis
Dai, Lu,Tai, Cui,Shen, Yaling,Guo, Yali,Tao, Fei
, p. 1 - 5 (2018)
1,4-Butanediol (BDO) biosynthesis from renewable resources is of increasing interest because of global energy and environmental problems. We have previously demonstrated the production of BDO from erythritol by whole-cell catalysis. Here, the effects of several variables on BDO production were investigated, including cell density, temperature, substrate concentration and pH. It was found that the maximum BDO production was obtained at cell density (OD600) of 30. Low temperature and weak alkaline environment were beneficial for the biotransformation. Regarding substrate concentration, 80?g/L of erythritol was found to be optimum for the bioconversion. Under the optimal conditions, the highest concentration of BDO reached 34.5?mg/L, resulting in 5.8-fold increment after optimization. These results will provide useful guidance for enhancing the bioconversion of erythritol to BDO.
Raney Ni-Si catalysts for selective hydrogenation of highly concentrated 2-butyne-1,4-diol to 2-butene-1,4-diol
Chen, Xiao,Zhang, Mingming,Yang, Kaixuan,Williams, Christopher T.,Liang, Changhai
, p. 1118 - 1126 (2014)
Raney Ni-Si catalysts were synthesized by treating Raney Ni with silane in a fluidized bed reactor and tested in the selective hydrogenation of 2-butyne-1,4-diol (BYD) at high concentration. Structural characterizations including XRD patterns, TEM images, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy show that Raney Ni-Si catalysts are composed of a Ni core surrounded by nickel silicides. These species transform from Ni-rich silicide (Ni2Si) to Si-rich silicide (NiSi2) with increasing silicification temperature from 250 °C to 450 °C. The insertion of Si atoms into Raney Ni catalysts decreased the catalytic activity, but significantly improved the selectivity to 2-butene-1,4-diol (BED). The beneficial effect of Si on the selectivity hydrogenation of BYD may be caused by the presence of Si at Ni-defect sites, and the formation of the surface nickel silicide that suppress the further hydrogenation of BED. Compared with the traditional Lindlar-type catalysts, such Raney Ni-Si materials can be used extensively in organic synthesis for selective hydrogenation of alkynes, avoiding the associated hazards of toxic additives.
Kinetics and mechanism of tetrahydrofuran synthesis via 1,4-butanediol dehydration in high-temperature water
Hunter, Shawn E.,Ehrenberger, Carolyn E.,Savage, Phillip E.
, p. 6229 - 6239 (2006)
We conducted an experimental investigation into the kinetics and mechanism of tetrahydrofuran synthesis from 1,4-butanediol via dehydration in high-temperature liquid water (HTW) without added catalyst at 200-350 °C. The reaction was reversible, with tetrahydrofuran being produced at an equilibrium yield of 84% (at 200 °C) to 94% (at 350 °C). The addition of CO2 to the reaction mixture increased the reaction rate by a factor of 1.9-2.9, because of the increase in acidity resulting from the formation and dissociation of carbonic acid. This increase was much less than that expected (factor of 37-60) from a previously suggested acid-catalyzed mechanism. This disagreement prompted experiments with added acid (HCl) and base (NaOH) to investigate the influence of pH on the reaction rate. These experiments revealed three distinct regions of pH dependence. At high and low pH, the dehydration rate increased with increasing acidity. At near-neutral pH, however, the rate was essentially insensitive to changes in pH. This behavior is consistent with a mechanism where H2O, in addition to H+, serves as a proton donor. This work indicates that the relatively high native concentration of H+ (large Kw), which has commonly been thought to lead to the occurrence of acid-catalyzed reactions in HTW without added catalyst, does not explain the dehydration of 1,4-butanediol in HTW without catalyst. Rather, H2O serves directly as the proton donor for the reaction.
Highly dispersed palladium nanoclusters incorporated in amino-functionalized silica spheres for the selective hydrogenation of succinic acid to γ-butyrolactone
You, Chenjia,Zhang, Chi,Chen, Lifang,Qi, Zhiwen
, p. 653 - 660 (2015)
Highly dispersed palladium nanoclusters incorporated on amino-functionalized silica sphere surfaces (Pd/SiO2-NH2) were fabricated by a simple one-pot synthesis utilizing 3-(2-aminoethylamino)propyltrimethoxysilane (AAPTS) as coordinating agent. Uniform palladium nanoclusters with an average size of 1.1 nm can be obtained during the co-condensation of tetraethyl orthosilicate and AAPTS owing to the strong interaction between palladium species and amino groups in AAPTS. The palladium particle size can be controlled by addition of AAPTS and plays a significant role in the catalytic performance. The Pd/SiO2-NH2 catalyst exhibits high catalytic activity for succinic acid hydrogenation with 100% conversion and 94% selectivity towards γ-butyrolactone using 1,4-dioxane as solvent at 240°C and 60 bar for 4 h. Moreover, the Pd/SiO2-NH2 catalyst is robust and readily reusable without loss of its catalytic activity.
Liquid-phase catalytic hydrogenation of 2-butyne-1,4-diol to 1,4-butanediol at atmospheric pressure on suspended catalysts
Pyatnitsyna,El'Chaninov
, p. 394 - 397 (2013)
The optimum parameters of hydrogenation of 2-butyne-1,4-diol to 1,4-butanediol on the suspended palladium and Ni-Raney catalysts at atmospheric pressure were found. In selected conditions a yield up to 90% of 1,4-butanediol was reached.
Analysis of drugs by pyrolysis. I. Selected ion monitoring combined with a pyrolysis method for the determination of carpronium chloride in biological samples.
Ohya,Sano
, p. 241 - 247 (1977)
In order to establish an analytical method for carpronium chloride, a parasympathomimetic agent, the pyrolysis reaction of carpronium chloride was examined in a g.c.m.s. system, which revealed that gamma-butyrolactone was produced directly from the drug as the main pyrolysis product. In the case of conversion of [2,2,3,3-2H4]carpronium chloride into the deuterated gamma-butyrolactone, 2H/1H scrambling was observed and confirmed to occur during the pyrolysis process of the deuterated compound. The proportion of gamma-[2H4]butyrolactone among the pyrolysis products was almost independent of the operating conditions, so [2,2,3,3-2H4]carpronium chloride was of practical use as an internal standard for selected ion monitoring. By incorporation of the pyrolysis reaction of carpronium chloride with selected ion monitoring and the use of [2,2,3,3-2H4]carpronium chloride as an internal standard, a rapid, sensitive and selective method was devised for the determination of the drug in biological samples. The method was utilized successfully for the biopharmaceutical studies of carpronium chloride in ma.
Hot Water Induces an Acid-Catalyzed Reaction in Its Undissociated Form
Nagai, Yasuharu,Matubayasi, Nobuyuki,Nakahara, Masaru
, p. 691 - 697 (2004)
Hot water in its undissociated form has been kinetically proven to induce a chemical reaction that does not undergo under ambient conditions in the absence of a strong acid. The water-induced and acid-catalyzed rate constants were separately determined for the dehydration of 1,4-butanediol by varying the oxonium ion (H+) concentration. It was found on the kinetic level over a wide range of temperature from moderate to supercritical that the undissociated form of water promotes the reaction at an effective acid concentration of 10-4-10-6 M. A strong density dependence of the reaction rate constant was further observed under supercritical condition, and is related to the anomalous temperature dependence of the rate constant near the critical point.
Selective Hydrogenation of Cyclic Ester to α,ω-Diol Catalyzed by Cationic Ruthenium Complexes with Trialkylphosphine Ligands
Hara, Yoshinori,Inagaki, Hiroko,Nishimura, Sugio,Wada, Keisuke
, p. 1983 - 1986 (1992)
Cyclic esters like γ-butyrolactone were smoothly hydrogenated in the presence of a series of ruthenium complexes with trialkylphosphine ligands under mild conditions to afford the corresponding α,ω-diols with high selectivity.The ruthenium complexes prepared in the presence of additional NH4PF6 or H3PO4 turned out to have the superior catalytic activity.
Pt nanoparticles over TiO2-ZrO2 mixed oxide as multifunctional catalysts for an integrated conversion of furfural to 1,4-butanediol
Li, Fengbo,Lu, Tao,Chen, Bingfeng,Huang, Zhijun,Yuan, Guoqing
, p. 252 - 258 (2014)
1,4-butanediol (BDO) is an important commodity chemical for manufacturing many basic chemicals and valuable polymers. Its current manufacturing processes are exclusively based on feedstocks derived from oil and natural gas. The biomass-to-BDO chemical transformation is via furfural, a key platform molecule from glucose and xylose. The integrated conversion involves two sequent reaction steps: selective oxidation of furfural to furanones and hydrogenation of the mixture of furanones to BDO. Platinum nanoparticles supported over TiO 2-ZrO2 perform well for both oxidation and hydrogenation steps and the total yield of BDO reaches 85.2%. The chemical composition and crystallinity of the mixed oxide support significantly affect the catalytic performance. The best catalyst is platinum supported over TiO 2-ZrO2 mixed oxide (Ti/Zr, 1:1) calcined at 823 K, which also exhibits good recoverability and recyclability in the five-run test.
Tracking Electrical Fields at the Pt/H2O Interface during Hydrogen Catalysis
Ryu, Jaeyune,Surendranath, Yogesh
, p. AR (2019)
We quantify changes in the magnitude of the interfacial electric field under the conditions of H2/H+ catalysis at a Pt surface. We track the product distribution of a local pH-sensitive, surface-catalyzed nonfaradaic reaction, H2 addition to cis-2-butene-1,4-diol to form n-butanol and 1,4-butanediol, to quantify the concentration of solvated H+ at a Pt surface that is constantly held at the reversible hydrogen electrode potential. By tracking the surface H+ concentration across a wide range of pH and ionic strengths, we directly quantify the magnitude of the electrostatic potential drop at the Pt/solution interface and establish that it increases by 60 mV per unit increase in pH. These results provide direct insight into the electric field environment at the Pt surface and highlight the dramatically amplified field existent under alkaline vs acidic conditions.
First example of borirane synthesis by α-olefins reaction with BCl3·SMe2 Catalyzed with (η5-C5H5)2TiCl2
Khusainova,Khafizova,Tyumkina,Dzhemilev
, p. 1517 - 1523 (2015)
New method was developed of the synthesis of 2-phenyl(alkyl, benzyl, phenoxy)-1-chloroboriranes via reaction of α-olefins with BCl3·SMe2 catalyzed by Cp2TiCl2. The method is based on the boracyclopropanes (boriranes) formation resulting from transmetallation of titanacyclopropanes arising from the reaction of α-olefins with Cp2TiCl2. The calculations were fulfilled of thermodynamic and activation parameters of possible reaction routes.
Converging conversion - using promiscuous biocatalysts for the cell-free synthesis of chemicals from heterogeneous biomass
Pick, André,Sieber, Volker,Sutiono, Samuel
, p. 3656 - 3663 (2021)
Production of chemicals from lignocellulosic biomass has been proposed as a suitable replacement to petrochemicals. However, one inherent challenge of biomass utilization is the heterogeneity of the substrate resulting in the presence of mixed sugars after hydrolysis. Fermentation of mixed sugars often leads to poor yield and generation of multiple by-products, thus complicating the subsequent downstream processing. System biocatalysis has thus been developed in recent years to address this challenge. In this work, several novel enzymes with broad substrate promiscuity were identified using a sequence-based discovery approach as suitable biocatalysts in a conversion ofd-xylose andl-arabinose, two major constituents of hemicellulose found in plant biomass. These promiscuous enzymes enabled simultaneous biotransformation ofd-xylose andl-arabinose to yield 1,4-butanediol (BDO) with a maximum production rate of 3 g L?1h?1and a yield of >95%. This model system was further adapted toward the production of α-ketoglutarate (2-KG) from the pentoses using O2as a cosubstrate for cofactor recycling reaching a maximum production rate of 4.2 g L?1h?1and a yield of 99%. To verify the potential applicability of our system, we attempted to scale up the BDO and 2-KG production fromd-xylose andl-arabinose. Simple optimization and reaction engineering allowed us to obtain BDO and 2-KG titers of 18 g L?1and 42 g L?1, with theoretical yields of >75% and >99%, respectively. One of the promiscuous enzymes identified together with auxiliary promiscuous enzymes was also suitable for stereoconvergent synthesis from a mixture ofd-glucose andd-galactose, predominant sugars found in food waste streams and microalgae biomass.
Reductive cleavage of tert-butyldimethylsilyl ether via intramolecular transfer of hydride
Saravanan, Parthasarathy,Gupta, Suparna,DattaGupta, Arpita,Gupta, Sonia,Singh, Vinod K.
, p. 2695 - 2699 (1997)
The cleavage of α-hydroxy tert-butyldimethylsilyl ether to diol takes place efficiently with LAH. It has been proposed that the reaction proceeds via intramolecular hydride transfer from the alkoxy aluminium hydride. In order to substantiate this, reduction of TBDMS ether with LAH in a variety of substrates was studied.
Catalytic hydrogenation of 2-butyne-1,4-diol to 2-butene-1,4-diol at atmospheric pressure in the liquid phase
Pyatnitsyna,El'chaninov,Savost'yanov
, p. 89 - 92 (2006)
Selective hydrogenation of 2-butyne-1,4-diol to 2-butene-1,4-diol on suspended palladium and Raney nickel catalysts at atmospheric pressure was studied. The optimal parameters of this reaction were determined. Samples containing 90% 2-butene-1,4-diol were
A synthesis method of diol
-
Paragraph 0043-0048, (2022/01/12)
The present invention belongs to the field of organic synthesis technology, specifically a synthesis method of a diol; the present invention by bis (trimethylsilyl) lithium amino catalytic lactone boronization of lactone to synthesize a variety of structure of the diol compound; specifically, under the bis (trimethylsilyl) amino lithium catalytic system, to a variety of lactone compounds and pinacol borane as raw materials, the preparation of diol compounds; the method of the present invention raw materials are of a wide range of sources or easy to prepare, easy to operate, selective and controllable, high yield, mild conditions, universality wide.
Hydroboration Reaction and Mechanism of Carboxylic Acids using NaNH2(BH3)2, a Hydroboration Reagent with Reducing Capability between NaBH4and LiAlH4
Wang, Jin,Ju, Ming-Yue,Wang, Xinghua,Ma, Yan-Na,Wei, Donghui,Chen, Xuenian
, p. 5305 - 5316 (2021/04/12)
Hydroboration reactions of carboxylic acids using sodium aminodiboranate (NaNH2[BH3]2, NaADBH) to form primary alcohols were systematically investigated, and the reduction mechanism was elucidated experimentally and computationally. The transfer of hydride ions from B atoms to C atoms, the key step in the mechanism, was theoretically illustrated and supported by experimental results. The intermediates of NH2B2H5, PhCH= CHCOOBH2NH2BH3-, PhCH= CHCH2OBO, and the byproducts of BH4-, NH2BH2, and NH2BH3- were identified and characterized by 11B and 1H NMR. The reducing capacity of NaADBH was found between that of NaBH4 and LiAlH4. We have thus found that NaADBH is a promising reducing agent for hydroboration because of its stability and easy handling. These reactions exhibit excellent yields and good selectivity, therefore providing alternative synthetic approaches for the conversion of carboxylic acids to primary alcohols with a wide range of functional group tolerance.
MOF-derived hcp-Co nanoparticles encapsulated in ultrathin graphene for carboxylic acids hydrogenation to alcohols
Dong, Mei,Fan, Weibin,Gao, Xiaoqing,Zhu, Shanhui
, p. 201 - 211 (2021/06/03)
Highly efficient conversion of carboxylic acids to valuable alcohols is a great challenge for easily corroded non-noble metal catalysts. Here, a series of few-layer graphene encapsulated metastable hexagonal closed-packed (hcp) Co nanoparticles were fabricated by reductive pyrolysis of metal-organic framework precursor. The sample pyrolyzed at 400 °C (hcp-Co@G400) presented outstanding performance and stability for converting a variety of functional carboxylic acids and its turnover frequency was one magnitude higher than that of conventional facc-centered cubic (fcc) Co catalysts. In situ DRIFTS spectroscopy of model reaction acetic acid hydrogenation and DFT calculation results confirm that carboxylic acid initially undergoes dehydroxylation to RCH2CO* followed by consecutive hydrogenation to RCH2CH2OH through RCH2COH*. Acetic acid prefers to vertically adsorb at hcp-Co (0 0 2) facet with a much lower adsorption energy than parallel adsorption at fcc-Co (1 1 1) surface, which plays a key role in decreasing the activation barrier of the rate-determining step of acetic acid dehydroxylation.
110-63-4 Process route
-
-
C36H60O30*C4H10O2

-
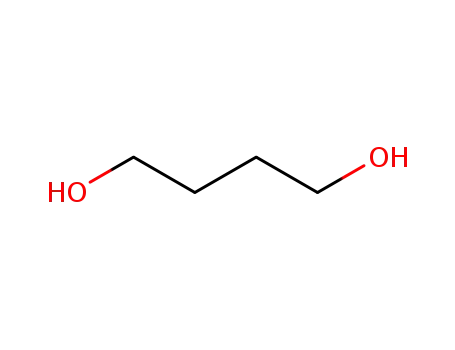
-
110-63-4
Butane-1,4-diol
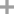
-
-
10016-20-3
alpha cyclodextrin
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
In
water;
at 25 ℃;
Equilibrium constant;
|
-
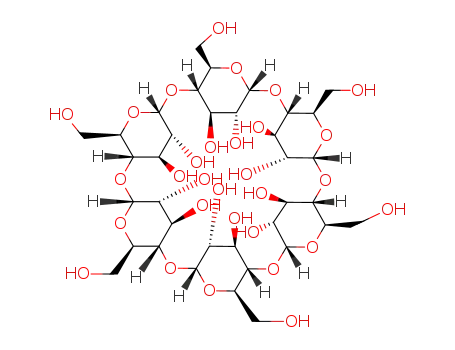
-
624-48-6
dimethyl cis-but-2-ene-1,4-dioate

-
-
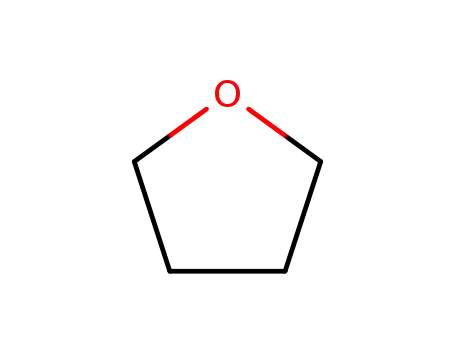
109-99-9,24979-97-3,77392-70-2
tetrahydrofuran

-
-
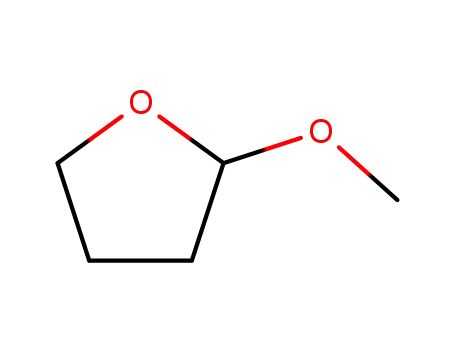
13436-45-8
2-methoxytetrahydrofuran

-
-
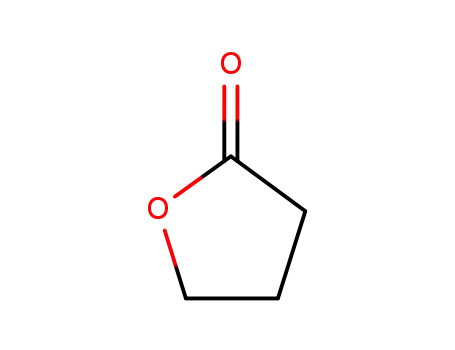
96-48-0
4-butanolide

-
-
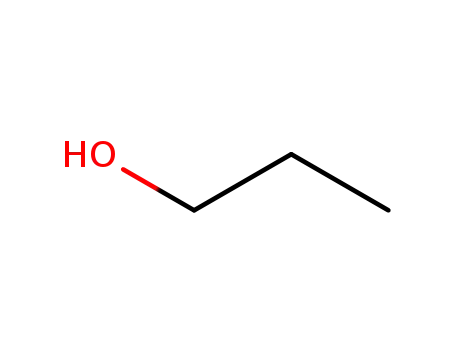
71-23-8
propan-1-ol

-
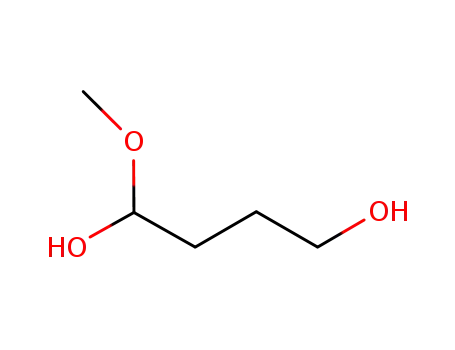
-
1-methoxy-1,4-butanediol

-
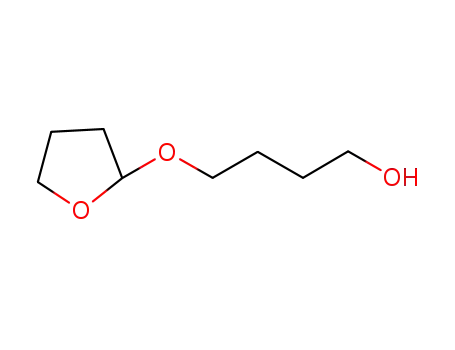
-
64001-06-5
2-(4'-hydroxybutoxy)-tetrahydrofuran

-
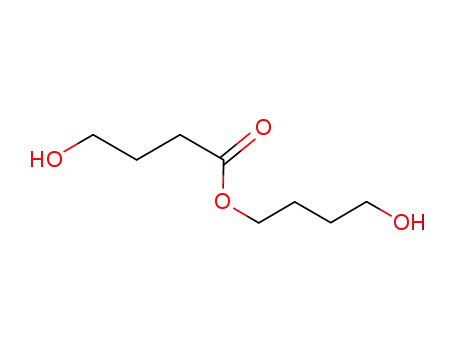
-
4-hydroxy-butanoic acid 4-hydroxybutyl ester

-

-
110-63-4
Butane-1,4-diol

-
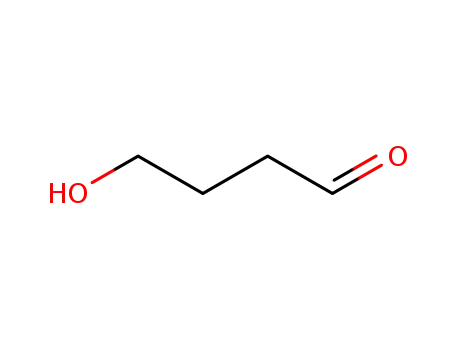
-
25714-71-0
4-hydroxybutyraldehyde

-
-
925-57-5
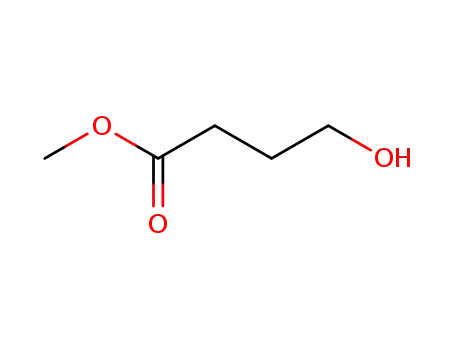
methyl 4-hydroxybutanoate

-
-
71-36-3
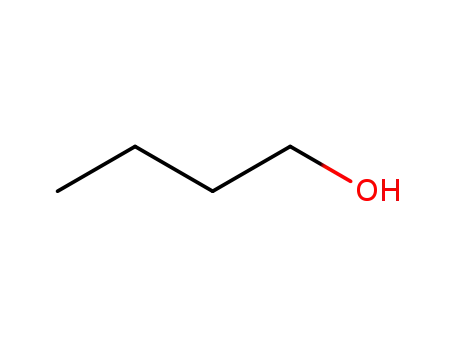
butan-1-ol
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
hydrogen;
at 190 ℃;
under 46504.7 Torr;
Gas phase;
|
79.1% 10.4% 5.3% |
110-63-4 Upstream products
-
1708-29-8
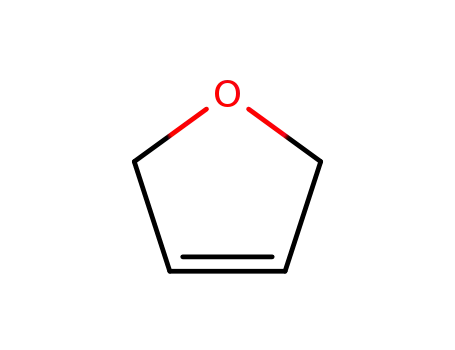
2,5-dihydrofuran
-
108-31-6
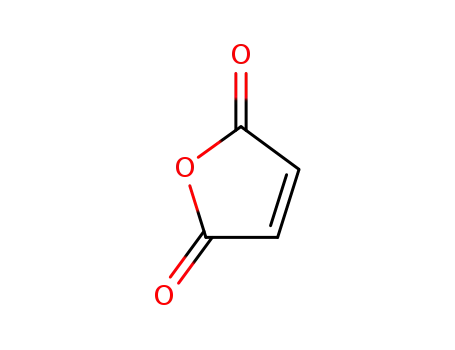
maleic anhydride
-
110-52-1
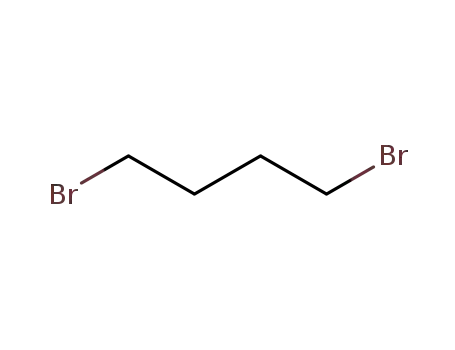
1,4-dibromo-butane
-
110-65-6
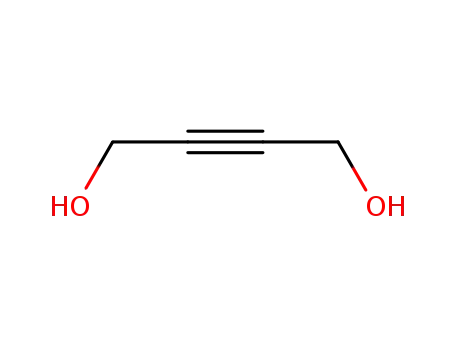
1,4-dihydroxybut-2-yne
110-63-4 Downstream products
-
13179-96-9
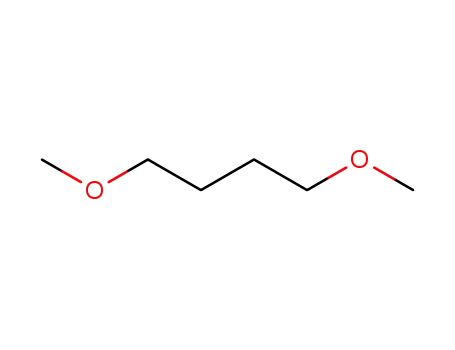
1,4-dimethoxybutane
-
5835-79-0
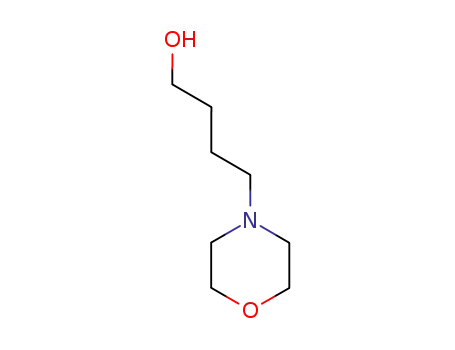
4-(1-hydroxypropyl)morpholine
-
53161-64-1
4,4'-butane-1,4-diyl-bis-morpholine
-
7191-20-0
2-phenyl-1,3,2-dioxaphosphepin-2-oxide