Product Details
9004-61-9 Properties
- Molecular Formula:(C14H21NO11)n
- Molecular Weight:403.31
- Appearance/Colour:White powder
- Vapor Pressure:0mmHg at 25°C
- Refractive Index:1.666
- Boiling Point:1274.4oC at 760 mmHg
- Flash Point:724.5oC
- PSA:399.71000
- Density:1.78 g/cm3
- LogP:-8.49480
9004-61-9 Usage
Forms and nomenclature
dietary supplements; face creams; serums; eye drops; injections
Hyaluronic Acid
Hyaluronic acid is a completely transparent, non-adhesive, water-soluble and grease-free acid mucopolysaccharide. Its molecular weight is between a few hundred thousand to millions, and it makes up the dermis layer of the skin. Its unique molecular structure and physicochemical properties has many important physiological functions inside the body, such as lubricating joints, adjusting vascular permeability, adjusting proteins, diffusing and transporting water electrolytes, and promoting wound healing. Hyaluronic acid has a unique water retention effect and has the best known natural moisturizing properties, making it the ideal natural moisturizer. Hyaluronic acid is an essential drug in ophthalmic “sticky surgeries”. It is used in cataract surgery, in which its sodium salt remains in the anterior chamber to maintain depth in the anterior chamber and ensure a clear surgical view. It reduces the occurences of postoperative inflammation and complications, thus improving the vision-correcting effects of the surgery. It is also used in complicated retinol detachment surgery. Hyaluronic acid has a low molecular weight and is considered the ideal natural moisturizing agent, so it is used as an additive in high-end makeup and as a moisturizer in creams, gels, lotions, masks, and serums. It is also used medically as a moisturizer to improve moisture retention and lubrication, and it also expands capillaries and improves skin health. For example, hyaluronic acid with a low molecular weight can be used as a lubricant in surgeries (such as knee surgery), while those with high molecular weight can be used as surgical lubricant and as a substitute for vitreous in ophthalmic surgery.
Benefits
Hyaluronic acid’s main functions include: Has excellent affinity to water and can regroup water within tissue for better retention and lubrication. Folds to form a three-dimensional network and produces physiological effects, including producing fluid resistance, maintaining water balance and bodily stability, influencing macromolecule solubility, structure, chemical balance and system osmotic pressure, preventing the spread of pathogens, and promote the condensation of collagen fiber secretory substances. Forms polymers with inseparable proteins to maintain tissue shape and size and to ensure reversible tissue compression resistance. Affects macrophages, adherent cells, lymph cells, and natural killer cells. Serves as an important part of interstitial fluid and is mainly metabolized in the liver. Liver fiber activity increases HA synthesis; combined with reduced function during cirrhosis, blood HA levels may increase abnormally.
Side effects
Studies show that hyaluronic acid with lower molecular weights penetrates deeper into the skin, which can cause inflammation.
Uses
Hyaluronic acid is a naturally derived, non - immunogenic, non - adhesive glycosaminoglycan that plays a prominent role in various wound - healing processes, as it as it is naturally angiogenic when degraded to small fragments. Hyaluronic acid promotes early inflammation which is critical for initiating wound healing, but then moderates later stages of the process, allowing matrix stabilization and reduction of long term inflammation. Hyaluronic acid is a main source for pharmaceutical, medical and cosmetic application.
Uses
Synovitis agent (veterinary).
Uses
hyaluronic acid is a glycosaminoglycan component. Hyaluronic acid occurs naturally in the dermis. It is thought to play a critical role in healthy skin by controlling the physical and biochemical characteristics of epidermal cells. It also regulates general skin activity, such as water content, elasticity, and the distribution of nutrients. Its water-absorption abilities and large molecular structure allow the epidermis to achieve greater suppleness, proper plasticity, and turgor. Hyaluronic acid is a natural moisturizer with excellent water-binding capabilities. In a solution of 2 percent hyaluronic acid and 98 percent water, the hyaluronic acid holds the water so tightly that it appears to create a gel. However, it is a true liquid in that it can be diluted and will exhibit a liquid’s normal viscous flow properties. When applied to the skin, hyaluronic acid forms a viscoelastic film in a manner similar to the way it holds water in the intercellular matrix of dermal connective tissues. This performance and behavior suggests that hyaluronic acid makes an ideal moisturizer base, allowing for the delivery of other agents to the skin. Manufacturers claim that the use of hyaluronic acid in cosmetics results in the need for much lower levels of lubricants and emollients in a formulation, thereby providing an essentially greaseless product. Furthermore, its ability to retain water gives immediate smoothness to rough skin surfaces and significantly improves skin appearance. For the benefits of hyaluronic acid to be realized in a cosmetic, the product needs to be applied on a regular basis as it is broken down in skin within 24 to 48 hours of application. note, this is not the case with hyaluronic acid injections as the technology used is different.
Definition
hyaluronic acid: A glycosaminoglycan(mucopolysaccharide) that ispart of the matrix of connective tissue.Hyaluronic acid binds cells togetherand helps to lubricate joints.It may play a role in the migration ofcells at wounds; this activity ceaseswhen hyaluronidase breaks downhyaluronic acid.
Definition
ChEBI: A mucopolysaccharide composed of N-acetylglucosamine and glucuronic acid subunits. It is found in the connective tissues of vertebrates.
Brand name
Equron [Veterinary] (Fort Dodge Animal Health); Legend (Bayer Animal Health); Synacid [Veterinary] (Schering-Plough Animal Health).
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Hyaluronic acid is a natural complex sugar of the glycosaminoglycan family and is a long-chain polymer containing repeating disaccharide units of Na-glucuronate-N-acetylglucosamine. Hyaluronic acid is indicated for use as a surgical aid in cataract extraction (intra-and extracapsular), IOL implantation, corneal transplant, glaucoma filtration and retinal attachment surgery. In surgical procedures in the anterior segment of the eye, instillation of hyaluronic acid serves to maintain a deep anterior chamber within corneal endothelium and other surrounding tissues. Furthermore, its viscoelasticity helps to push back the vitreous face and prevent formation of a postoperative flat chamber. In posterior segment surgery hyaluronic acid serves as a surgical aid to gently separate, maneuver and hold tissues. Hyaluronic acid creates a clear field of vision thereby facilitating intra- and post-operative inspection of the retina and photocoagulation.
InChI:InChI=1/C28H44N2O23/c1-5(33)29-9-18(11(35)7(3-31)47-25(9)46)49-28-17(41)15(39)20(22(53-28)24(44)45)51-26-10(30-6(2)34)19(12(36)8(4-32)48-26)50-27-16(40)13(37)14(38)21(52-27)23(42)43/h7-22,25-28,31-32,35-41,46H,3-4H2,1-2H3,(H,29,33)(H,30,34)(H,42,43)(H,44,45)/t7-,8-,9-,10-,11-,12-,13+,14?,15-,16-,17-,18-,19?,20+,21+,22?,25?,26+,27+,28-/m1/s1
9004-61-9 Relevant articles
Peroxynitrite (ONOO-) generation from the HA-TPP@NORM nanoparticles based on synergistic interactions between nitric oxide and photodynamic therapies for elevating anticancer efficiency
Jiang, Dawei,Yue, Tao,Wang, Guichen,Wang, Chaochao,Cao, Hongliang,Gao, Yun,Chen, Chao
, p. 162 - 170 (2019/12/26)
Due to biological safety and negligible toxicity, nitric oxide (NO) therapy has gained increasing interest in the field of cancer therapy during the past few years. However, individual NO cancer therapy normally exhibited limited therapeutic efficiency. In order to acquire satisfactory therapeutic outcomes, the NO therapy is usually combined with other therapeutic treatments, mostly chemotherapy. Herein, we constructed HA-TPP@NORM nanoparticles based on the co-assembly of an NO donor (NORM) and tetraphenylporphyrin (TPP)-modified hyaluronic acid, which can efficiently generate a highly biocidal molecule of peroxynitrite (ONOO-) via the synergistic interactions of the nitric oxide (NO) therapy and photodynamic therapy (PDT) to enhance the cancer therapeutic efficiency. In addition, MTT results exhibited that without light irradiation, the HA-TPP@NORM nanoparticles have favourable biocompatibility with the cell viability above 95% at the maximum TPP concentration (20 μg mL-1). Under simultaneous irradiation with 365 nm and 650 nm light, ONOO- can be efficiently produced in cancer cells via the direct coupling reaction of the generated NO and superoxide anion radical (O2-), which significantly enhanced the anticancer effect, when compared with individual NO therapy or PDT therapy. Therefore, the HA-TPP@NORM nanoparticles may provide a new insight into the design of efficiently NO-related cancer therapeutic systems.
COMPOSITION COMPRISING HYALURONIC ACID AND/OR ITS SALTS FOR TREATMENT OF ATOPIC DERMATITIS
-
Page/Page column 8; 10, (2008/12/06)
Provided is a composition for prevention and treatment of atopic dermatitis, comprising hyaluronic acid and/or a salt thereof, and preferably resveratrol. The composition has therapeutic effects on amelioration and treatment of atopic dermatitis which is an allergic disease.
PHARMACEUTICAL FORMULATIONS
-
Page/Page column 17, (2010/02/15)
The present invention relates to salts of a biodegradable polymeric sugars comprising acidic groups and a pharmaceutically active agent comprising one or more basic groups, and to pharmaceutical formulations of said salts adapted for administration by inhalation.Λa présente invention a trait à des sels d''un sucre polymérique biodégradable comportant des groupes acides et un agent pharmaceutiquement actif comportant un ou des groupes basiques, et à des formulations pharmaceutiques desdits sels adaptées pour une administration par inhalation.
Method for producing alkyl-esterified glycosaminoglycan
-
Page/Page column 5, (2008/06/13)
A method for producing an alkyl-esterified glycosaminoglycan, which comprises the step of allowing a trialkylsilyldiazoalkane to act on a glycosaminoglycan to perform alkyl-esterification of carboxyl groups of the glycosaminoglycan, and an alkyl-esterified glycosaminoglycan having a property that it is not substantially degraded by a glycosaminoglycan degrading enzyme such as hyaluronidase are provided.
9004-61-9 Process route
-
![2-methyl-[1,2-di-deoxy-3-O-(sodium β-D-glucopyranosyluronate)-α-D-glucopyrano]-[2,1,d]-2-oxazoline](/upload/2023/2/3c7a27a0-634b-456e-8aa0-594145c1c4d4.png)
-
2-methyl-[1,2-di-deoxy-3-O-(sodium β-D-glucopyranosyluronate)-α-D-glucopyrano]-[2,1,d]-2-oxazoline

-
hyaluronic acid
-
9004-61-9
hyaluronic acid
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
Carbonate buffer; ovine testicular hyaluronidase;
In
water-d2;
at 30 ℃;
for 36h;
pH=7.1;
|
52% |
-
hyaluronic acid, sodium salt
-
hyaluronic acid, sodium salt

-
hyaluronic acid
-
9004-61-9
hyaluronic acid
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
Amberlyte IR 120, H(+)-form resin;
In
water;
|
9004-61-9 Upstream products
-
9067-32-7
sodium hyaluronate
9004-61-9 Downstream products
-
9067-32-7
sodium hyaluronate
-
90-76-6
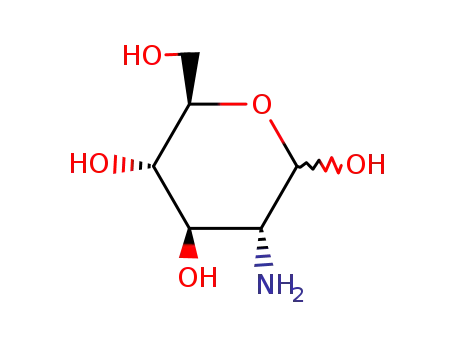
2-deoxy-2-amino glucose
-
6556-12-3
D-glucuronic acid