Product Details
593-84-0 Properties
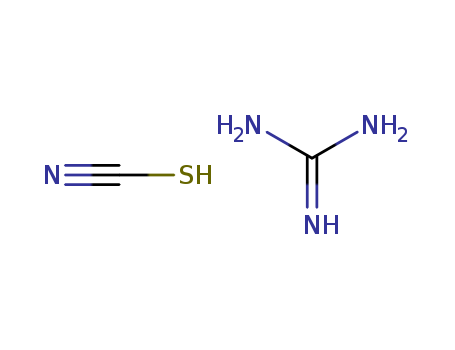
- Molecular Formula:C2H6N4S
- Molecular Weight:118.162
- Appearance/Colour:White cryst. powder
- Vapor Pressure:0.00206mmHg at 25°C
- Melting Point:120-122 °C(lit.)
- Refractive Index:n20/D 1.482
- Boiling Point:132.9 °C at 760 mmHg
- PKA:12.5[at 20 ℃]
- Flash Point:34.2 °C
- PSA:138.48000
- Density:1.103 g/mL at 20 °C
- LogP:0.73618
593-84-0 Usage
Description
Guanidine thiocyanate is one of the cheapest and easiest to prepare of the guanidine salts. Guanidine Thiocyanate is an ultrapure, molecular biology grade reagent. It is free of detectable nuclease and protease activity and is a strong protein denaturant, as both the guanidinium cation and the thiocyanate anion are chaotropic agents. It is provided in one bottle containing 500 g. It is recommended for isolation of RNA, especially for tissues such as pancreas with high levels of RNase activity. In solution, it is known as guanidinium thiocyanate. Guanidine Thiocyanate is thoroughly tested for contaminating nonspecific endonuclease, exonuclease, and RNase activity.
Uses
Guanidine thiocyanate is a potent protein denaturant (stronger than guanidine HCl) often used in the isolation of intact ribonucleic acid to eliminate RNase activity. RNase can recover activity after boiling, but is irreversibly inactivated in a 4 M solution of guanidine thiocyanate. Such solutions, to which the reducing agent b-mercaptoethanol is often added, are used to inactivate RNAse when isolating RNA from tissues that are rich in RNase, such as liver. Total nuclear and cytoplasmic RNA may be isolated this way. A protocol for extracting RNA with guanidine isothiocyanate has been published.In the presence of guanidine thiocyanate, proteins dissolve readily, cellular structures disintegrate and nucleoproteins dissociate from nucleic acids, as protein secondary structure is lost.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Guanidine thiocyanate is a denaturing agent and is used routinely in RNA isolation. It is used as a storage buffer for whole blood samples. Guanidine thiocyanate inactivates nucleases and is ideal for storing and freezing fecal samples for DNA studies. It is used in combination with phenol?chloroform in RNA extraction.
Toxicity evaluation
Guanidine thiocyanate is used commercially as a disinfectant and a general protein denaturant but its more common use is in the extraction of DNA and RNA in molecular biology. Нere are no reports of guanidine thiocyanate toxicity from oral ingestion. Toxicity of di??erent thiocyanate compounds other than guanidine thiocyanate has been described. Potassium thiocyanate was used over 50 years ago for the treatment of hypertension and its toxicity appears to cause a neurological disorder consisting of generalized weakness, delirium and a decrease level of consciousness. Reports of thiocyanate toxicity from nitroprusside use for hypertension in the setting of renal impairment/failure have also been reported as thiocyanate is renally cleared. In a fatal deliberate ingestion of a herbicide which contained ammonium thiocyanate and aminotriazole, a 54 year old man presented with coma and cardiovascular collapse although the relative contributions of the two herbicides to the clinical toxicity is unknown.
Chemical Properties
White cryst.powder
Uses
Potent protein denaturant used in isolation of intact DNA, RNA.
Uses
Guanidine thiocyanate is a useful tool for RNA isolation and protein solubilization. It is involved in the quantification of mRNA from hepatocytes. It acts as a medium for blood smaple lystae in order to maintain the integrity of nucleic acid. It is a chaotropic agent, mainly involved in the extraction of DNA and RNA. It is utilized to deactivate the influenza virus.
Uses
Guanidine thiocyanate has been used as a component of the stabilization buffer for RNA lysis. It can be used for deactivation of endogenous RNases leading to denaturation of nucleoprotein complexes. It is also suitable for denaturation of macromolecules such as nucleic acids and proteins and for RNA isolation.
General Description
Guanidine thiocyanate is chaotropic salts which lyse cells and along with nuclease binding matrix it is also seen to inhibit nuclease activity during extraction of DNA. It works as a strong RNase inhibitor in extraction buffers.
Hazard
Irritant.
Flammability and Explosibility
Notclassified
Biochem/physiol Actions
Guanidine thiocyanate (GTC) plays a role in protein denaturation. It is involved in separation of ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) from ribosomes and denatures ribonuclease (RNase). GTC has been studied in the unfolding and refolding of fluorescent proteins (FP). It can be used along with phenol and chloroform for extraction of RNA.
InChI:InChI=1/C2H4N4S/c3-1-7-6-2(4)5/h(H4,4,5,6)
593-84-0 Relevant articles
Kinetics of thermal decomposition of thiourea
Timchenko,Novozhilov,Slepysheva
, p. 1046 - 1050 (2007/10/03)
Thermal decomposition of thiourea in a melt was studied by isothermal and nonisothermal kinetic methods. The influence of the gas flow rate over the melt, layer thickness, and other factors on the process was elucidated. The kinetic parameters of the steps of formation of guanidinium thiocyanate and solid cyclic compounds, products of thiourea thermolysis, were determined.
593-84-0 Process route
-
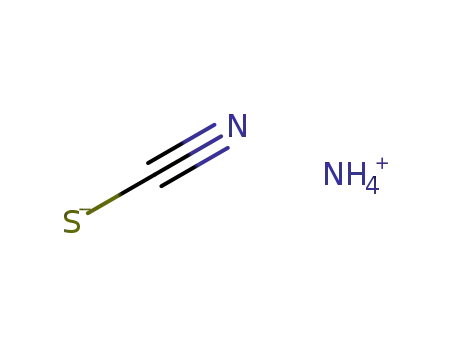
-
ammonium thiocyanate
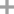
-
-
127099-85-8,780722-26-1
dicyandiamide

-
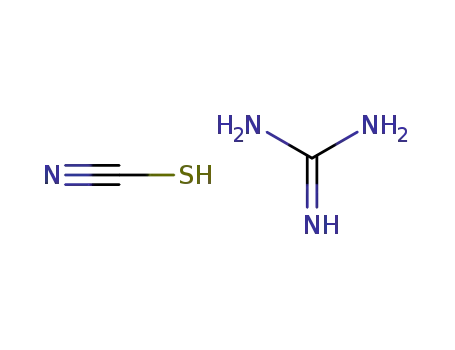
-
593-84-0,5341-59-3
guanidinium thiocyanate
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
In
melt;
55 part of dicyanodiamide reacted with 100 part of NH4SCN;
|
90% |
|
In
melt;
55 part of dicyanodiamide reacted with 100 part of NH4SCN;
|
90% |
-

-
ammonium thiocyanate

-

-
593-84-0,5341-59-3
guanidinium thiocyanate
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
heating over temp. of formation of (NH4)2CS;
|
|
|
byproducts: NH3, CS2; 220°C;
|
|
|
With
ammonia; ammonium chloride;
300°C;
|
25-30 |
|
With
ammonia; lead(II) chloride;
300°C;
|
<95 |
|
In
neat (no solvent);
20 h at 180-190°C; melt extd. with water; evapn.; crystn.;
|
|
|
heating over temp. of formation of (NH4)2CS;
|
593-84-0 Upstream products
-
108-78-1
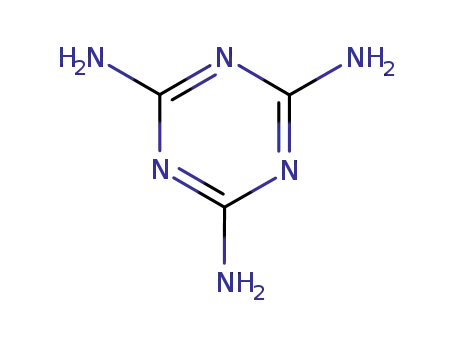
2,4,6-triamino-s-triazine
-
1147550-11-5
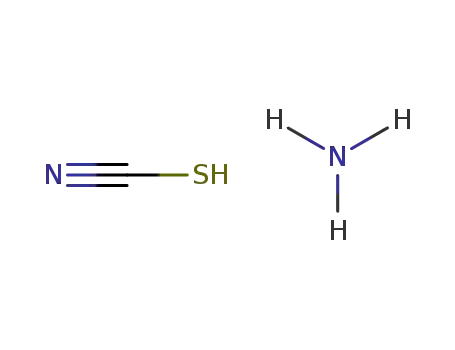
ammonium thiocyanate
-
420-04-2
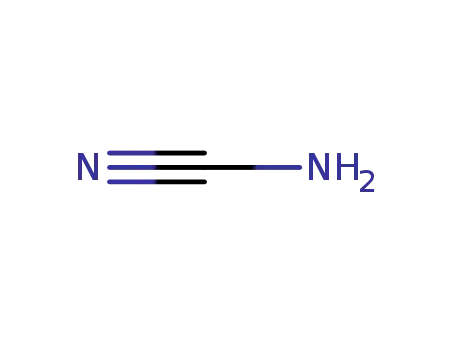
CYANAMID
-
127099-85-8
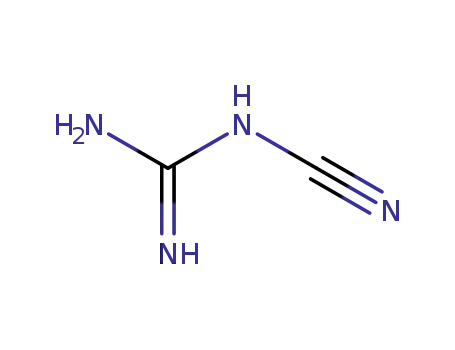
N-Cyanoguanidine
593-84-0 Downstream products
-
19010-48-1
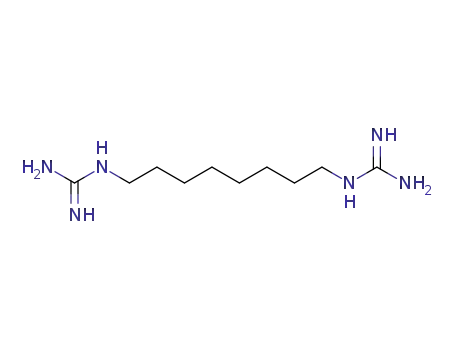
1,8-Diguanidino-octan
-
111-23-9
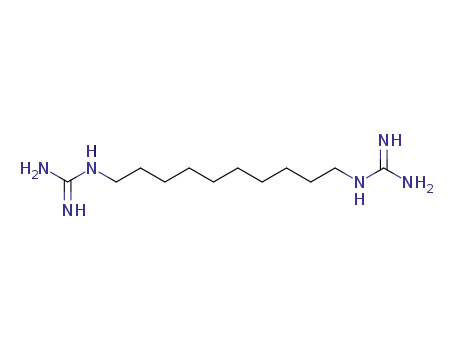
N,N'''-1,10-decanediylbisguanidine
-
18340-59-5
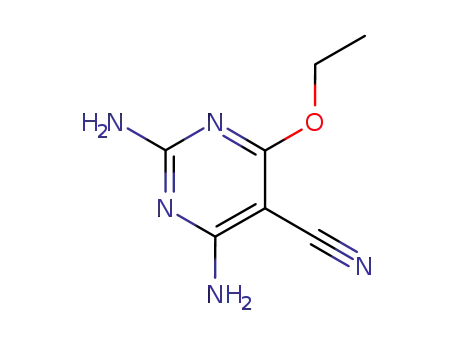
2,4-Diamino-6-ethoxy-5-cyan-pyrimidin
-
46463-06-3
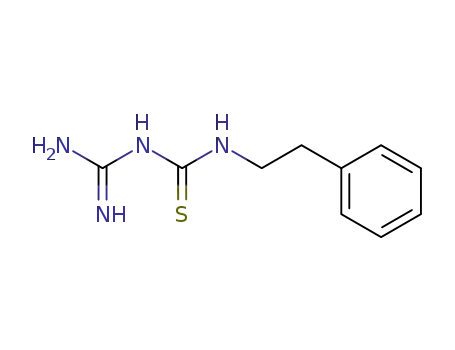
N-carbamimidoyl-N'-phenethyl-thiourea