Product Details
|
61-54-1 Name |
|
|
Name |
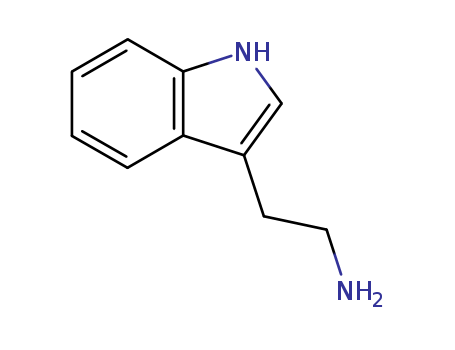
Tryptamine |
|
Synonym |
(Amino-2 ethyl)-3 indole;(amino-2ethyl)-3indole;3-(2-aminoethyl)-indol;3-Indoleethylamine;beta-(3-Indolyl)ethylamine;Indol-3-ethylamine;Indole, 3-(2-aminoethyl)-;Tryptamin |
|
61-54-1 Biological Activity |
|
|
Description |
Tryptamine is a monoamine alkaloid, similar to other trace amines, is believed to play a role as a neuromodulator or neurotransmitter. |
|
Related Catalog |
Natural Products >> Alkaloid Research Areas >> Others |
|
Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
|
References |
[1]. Jones RS, et al. Tryptamine: a neuromodulator or neurotransmitter in mammalian brain? Prog Neurobiol. 1982;19(1-2):117-39. |
|
61-54-1 Chemical & Physical Properties |
|
|
Melting point |
113-116 °C(lit.) |
|
Boiling point |
378.8±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
|
Density |
1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|
Molecular Formula |
C10H12N2 |
|
Molecular Weight |
160.216 |
|
Flash Point |
187.7±8.1 °C |
|
PSA |
41.81000 |
|
LogP |
1.38 |
|
Exact Mass |
160.100052 |
|
Vapour Pressure |
0.0±0.8 mmHg at 25°C |
|
Index of Refraction |
1.669 |
|
Water Solubility |
negligible |
|
61-54-1 Description |
|
Tryptamine is a monoamine alkaloid that can be synthesized by decarboxylation of the amino acid tryptophan. Notably, tryptamine can be found in fungi, plants, Amphibia, animals, and microbes. Tryptamine has an indole ring structure and a fused double ring that is composed of a benzene ring and a pyrrole ring, linked to an amino group by 2-carbon side chain. The indole ring is the vital nucleus of many complex natural products that have significance in drug discovery as well as some synthetic and non-synthetic drugs that are based on tryptamine skeleton. The chemical’s distinct structure is an approximation to the neurotransmitter serotonin as well-known drugs and hallucinogens. Tryptamine’s significance as psychedelic drugs, neuromodulator, and neurotransmitter is well understood due to its presence in mammalian brain in small amounts. |
|
61-54-1 Uses |
|
Tryptamine is a monoamine alkaloid found in plants. Tryptamine is commonly used in the preparation of biologically active compounds such as neurotransmitters and psychedelics. |