Product Details
|
593-84-0 Name |
|
|
Name |
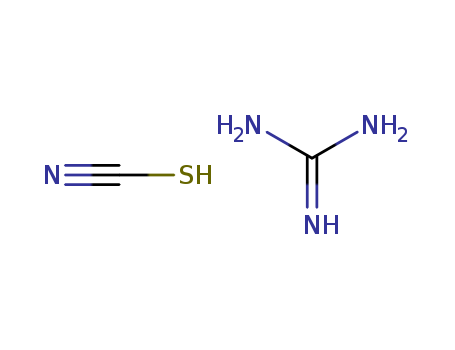
Guanidine thiocyanate |
|
Synonym |
GTC;GUANIDINE THIOCYANATE;GUANIDINE HYDROTHIOCYANATE;GUANIDINE ISOTHIOCYANATE;GUANIDINE MONOTHIOCYANATE;GUANIDINE RHODANIDE;GUANIDINIUM THIOCYANATE;GUANIDINIUM ISOTHIOCYANATE |
|
593-84-0 Biological Activity |
|
|
Description |
Guanidine thiocyanate is a chaotropic agent. Guanidine thiocyanate can be used as a protein denaturant and a nucleic acid protector in the extraction of DNA and RNA from cells[1]. |
|
Related Catalog |
Research Areas >> Others |
|
Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
|
References |
[1]. Mason PE, et al. The hydration structure of guanidinium and thiocyanate ions: implications for protein stability in aqueous solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(8):4557-4561. |
|
593-84-0 Chemical & Physical Properties |
|
|
Melting point |
120-122 °C(lit.) |
|
Boiling point |
132.9ºC at 760 mmHg |
|
Density |
1.103 g/mL at 20 °C |
|
Molecular Formula |
C2H6N4S |
|
Molecular Weight |
118.16 |
|
Flash Point |
34.2ºC |
|
PSA |
138.48000 |
|
LogP |
0.73618 |
|
Exact Mass |
118.031319 |
|
Index of Refraction |
n20/D 1.482 |
|
Storage condition |
Store at RT. |
|
Stability |
Stability Stable, but light sensitive. Incompatible with acids (contact releases very toxic gas), strong oxidising agents. |
|
Water Solubility |
H2O: 6 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless |
|
593-84-0 Description |
|
Guanidine thiocyanate is one of the cheapest and easiest to prepare of the guanidine salts. Guanidine Thiocyanate is an ultrapure, molecular biology grade reagent. It is free of detectable nuclease and protease activity and is a strong protein denaturant, as both the guanidinium cation and the thiocyanate anion are chaotropic agents. It is provided in one bottle containing 500 g. It is recommended for isolation of RNA, especially for tissues such as pancreas with high levels of RNase activity. In solution, it is known as guanidinium thiocyanate. Guanidine Thiocyanate is thoroughly tested for contaminating nonspecific endonuclease, exonuclease, and RNase activity. |
|
593-84-0 Uses |
|
Guanidine thiocyanate is a potent protein denaturant (stronger than guanidine HCl) often used in the isolation of intact ribonucleic acid to eliminate RNase activity. RNase can recover activity after boiling, but is irreversibly inactivated in a 4 M solution of guanidine thiocyanate. Such solutions, to which the reducing agent b-mercaptoethanol is often added, are used to inactivate RNAse when isolating RNA from tissues that are rich in RNase, such as liver. Total nuclear and cytoplasmic RNA may be isolated this way. A protocol for extracting RNA with guanidine isothiocyanate has been published. In the presence of guanidine thiocyanate, proteins dissolve readily, cellular structures disintegrate and nucleoproteins dissociate from nucleic acids, as protein secondary structure is lost. |